Azure Apps: 7 Ultimate Power Tips for 2024
Looking to master Azure apps? Discover how Microsoft’s cloud platform is revolutionizing application development with unmatched scalability, security, and integration. Whether you’re a developer or IT leader, this guide unlocks everything you need to know.
What Are Azure Apps and Why They Matter

Azure apps refer to applications built, deployed, and managed using Microsoft Azure’s cloud computing platform. These aren’t just ordinary apps—they’re cloud-native, scalable, and designed for enterprise-grade performance. From web apps to mobile backends and microservices, Azure apps power modern digital transformation.
Defining Azure Apps in the Cloud Ecosystem
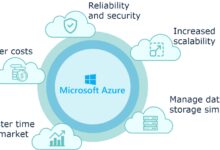
Azure apps encompass a broad range of services under the Microsoft Azure umbrella, including App Services, Functions, Logic Apps, and Container Instances. These tools allow developers to build, deploy, and scale applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. According to Microsoft, over 95% of Fortune 500 companies use Azure for their cloud needs, highlighting its dominance in enterprise environments.
- Azure apps are not limited to one type of application—they support web, mobile, API, and serverless workloads.
- They integrate seamlessly with other Azure services like Azure Active Directory, Azure DevOps, and Azure Monitor.
- Developers can use any programming language, including .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and PHP.
“Azure is not just a cloud platform; it’s a comprehensive ecosystem for building the future of applications.” — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
Key Components of Azure App Services
Azure App Services is the cornerstone of Azure apps, offering a fully managed platform for hosting web applications. It supports continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD), auto-scaling, and built-in security features. With App Services, developers can focus on code rather than infrastructure management.
- Web Apps: Host websites and web applications with support for custom domains and SSL.
- API Apps: Expose business logic as RESTful APIs with built-in Swagger support.
- Mobile Apps: Enable backend services for mobile apps with offline sync and push notifications.
For more details, visit the official Azure App Service documentation.
Top 7 Benefits of Using Azure Apps
Organizations worldwide are shifting to Azure apps for compelling reasons. From cost savings to enhanced security, the advantages are transformative. Let’s explore the seven most impactful benefits that make Azure apps a top choice for modern development.
1. Scalability That Grows With Your Business
One of the standout features of Azure apps is their ability to scale automatically. Whether you’re experiencing a sudden spike in traffic or planning for long-term growth, Azure’s auto-scaling capabilities ensure your app remains responsive and available.
- Vertical scaling: Increase instance size (e.g., from Basic to Premium).
- Horizontal scaling: Add more instances to handle load.
- Scheduled scaling: Adjust capacity based on predictable traffic patterns (e.g., holiday sales).
This elasticity means you only pay for what you use, making it a cost-effective solution for startups and enterprises alike.
2. Enterprise-Grade Security and Compliance
Security is non-negotiable in today’s digital landscape. Azure apps come with built-in security features such as DDoS protection, network isolation, and identity management via Azure AD. Additionally, Microsoft complies with over 140 global certifications, including GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures only authorized users can access resources.
- Managed identities eliminate the need to store credentials in code.
- Integration with Azure Security Center provides real-time threat detection.
Learn more about Azure’s security posture at Microsoft Trust Center.
3. Seamless Integration with DevOps Tools
Azure apps are designed for modern development workflows. With native integration into Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Jenkins, teams can automate builds, tests, and deployments. This accelerates time-to-market and improves code quality.
- CI/CD pipelines can be set up in minutes using templates.
- Blue-green deployments minimize downtime during updates.
- Rollback capabilities ensure quick recovery from failed releases.
This tight integration makes Azure apps ideal for agile and DevOps-driven organizations.
How to Build Your First Azure App
Getting started with Azure apps is easier than you think. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, this step-by-step guide will help you deploy your first application on Azure.
Step 1: Set Up Your Azure Account
To begin, you’ll need an Azure account. Microsoft offers a free tier with $200 in credits for new users, valid for 30 days. This is perfect for testing and learning.
- Visit Azure Free Account to sign up.
- Verify your identity with a credit card (no charges unless you upgrade).
- Access the Azure portal at portal.azure.com.
Once logged in, you’ll see a dashboard with all available services.
Step 2: Create a Web App in Azure App Service
Now, let’s deploy a simple web app. In the Azure portal, search for “App Services” and click “Create.” Choose your subscription, resource group, and region. Then, configure your app name and runtime stack (e.g., .NET, Node.js).
- Select a pricing tier—start with the Free or Shared tier for testing.
- Enable Application Insights for monitoring.
- Click “Review + Create” and then “Create” to deploy.
Deployment takes just a few minutes. Once complete, you can access your app via the assigned URL (e.g., https://yourappname.azurewebsites.net).
Step 3: Deploy Code Using GitHub
To automate deployments, connect your app to a GitHub repository. In the App Service menu, go to “Deployment Center” and select GitHub as the source. Authorize Azure to access your repositories and choose the branch to deploy.
- Every push to the selected branch triggers a new deployment.
- View deployment logs in real time.
- Use GitHub Actions for advanced workflows like testing and staging.
This setup enables continuous delivery, a key practice in modern software development.
Azure Apps vs. Competitors: A Strategic Comparison
While AWS and Google Cloud are major players, Azure apps offer unique advantages, especially for organizations already using Microsoft products. Let’s compare Azure with its top competitors across key dimensions.
Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem
Azure apps shine in environments that rely on Microsoft tools like Office 365, Dynamics 365, and Active Directory. This deep integration reduces friction and enhances productivity.
- SAML-based single sign-on (SSO) with Azure AD simplifies user management.
- Power Platform integration allows low-code app development.
- Hybrid cloud scenarios are easier with Azure Stack and Azure Arc.
For enterprises with a Microsoft footprint, Azure apps provide a cohesive experience that AWS or GCP can’t match.
Pricing and Cost Management
Azure offers competitive pricing with flexible options. The Azure Pricing Calculator helps estimate costs based on usage. Compared to AWS, Azure often provides better value for Windows-based workloads and hybrid deployments.
- Reserved Instances offer up to 72% savings on long-term commitments.
- Spot VMs reduce costs for non-critical, interruptible workloads.
- Azure Hybrid Benefit allows using existing Windows Server licenses for up to 40% savings.
Additionally, Azure Cost Management provides detailed insights and alerts to prevent budget overruns.
Global Reach and Data Residency
Azure has 60+ regions worldwide—more than any other cloud provider. This global presence ensures low latency and compliance with data sovereignty laws.
- Data residency is guaranteed within the region you choose.
- Edge Zones bring cloud services closer to users and devices.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) accelerates content delivery globally.
This makes Azure apps ideal for multinational organizations with strict regulatory requirements.
Advanced Features of Azure Apps
Beyond basic hosting, Azure apps offer advanced capabilities that empower developers to build smarter, more resilient applications. These features are what set Azure apart in the competitive cloud landscape.
Serverless Computing with Azure Functions
Azure Functions enables event-driven, serverless computing. You write small pieces of code (functions) that run in response to triggers like HTTP requests, timers, or queue messages.
- No need to manage servers—Azure handles scaling automatically.
- Pay only for execution time (per millisecond).
- Supports multiple languages and integrates with Logic Apps for workflows.
For example, you can trigger a function when a file is uploaded to Azure Blob Storage, automatically processing and analyzing the data.
Microservices with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
For complex applications, Azure apps support microservices architecture via AKS. AKS simplifies the deployment, management, and scaling of containerized applications using Kubernetes.
- Integrated with Azure Monitor for performance tracking.
- Supports autoscaling, self-healing, and rolling updates.
- Can be combined with Azure Service Mesh for advanced traffic management.
AKS is ideal for teams adopting cloud-native development practices.
AI and Cognitive Services Integration
Azure apps can leverage AI through Cognitive Services APIs. These include vision, speech, language, and decision-making models that can be embedded into applications.
- Add facial recognition to a security app.
- Implement natural language processing for chatbots.
- Use anomaly detection for predictive maintenance.
This integration allows developers to build intelligent apps without deep AI expertise.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While Azure apps offer powerful capabilities, users may face challenges during adoption. Understanding these pitfalls and how to address them is crucial for success.
Complexity of Configuration and Management
The breadth of Azure services can be overwhelming for new users. Misconfigurations can lead to security vulnerabilities or performance issues.
- Solution: Use Azure Blueprints to enforce organizational standards.
- Leverage Azure Policy to audit and enforce compliance.
- Train teams with Microsoft Learn modules.
Proper governance reduces risk and ensures consistent deployments.
Cost Overruns Due to Unmonitored Usage
Without proper monitoring, cloud costs can spiral out of control. Idle resources or over-provisioned instances contribute to unnecessary expenses.
- Solution: Enable Azure Cost Management + Billing alerts.
- Use tags to categorize resources by department, project, or environment.
- Regularly review and decommission unused resources.
Proactive cost control ensures optimal ROI from Azure apps.
Latency Issues in Global Deployments
Applications serving users across continents may experience latency if not deployed strategically.
- Solution: Deploy apps in multiple Azure regions using Traffic Manager.
- Use Azure Front Door for global load balancing and SSL offload.
- Cache static content with Azure CDN.
These strategies improve user experience and application performance.
Future Trends Shaping Azure Apps
The future of Azure apps is being shaped by emerging technologies and evolving user demands. Staying ahead of these trends ensures your applications remain competitive and future-proof.
Rise of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Microsoft is heavily investing in Power Apps, a low-code platform that integrates with Azure apps. This allows business users to build applications without writing code, accelerating digital transformation.
- Connect to Azure SQL, SharePoint, and Dynamics 365.
- Deploy apps across web and mobile devices.
- Enforce security with Azure AD and data loss prevention policies.
This trend democratizes app development and reduces dependency on IT teams.
Edge Computing and IoT Integration
Azure apps are expanding beyond the cloud with Azure IoT Edge and Azure Sphere. These services enable processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
- Run AI models on edge devices for real-time insights.
- Secure IoT devices with hardware-based trust.
- Integrate with Azure Digital Twins for smart environments.
Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics are leveraging this for predictive maintenance and automation.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Initiatives
Microsoft has committed to being carbon negative by 2030. Azure apps contribute to this goal by optimizing energy efficiency and enabling sustainable application design.
- Azure regions use renewable energy sources.
- Tools like Azure Sustainability Calculator help estimate carbon impact.
- Efficient resource utilization reduces environmental footprint.
Sustainable cloud practices are becoming a competitive advantage.
Best Practices for Managing Azure Apps
To maximize the value of Azure apps, follow these best practices for deployment, monitoring, and optimization.
Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Use tools like Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates or Terraform to define your infrastructure in code. This ensures consistency, version control, and repeatability.
- Store templates in source control (e.g., GitHub).
- Use parameter files for environment-specific configurations.
- Automate deployments with CI/CD pipelines.
IaC reduces manual errors and accelerates provisioning.
Enable Comprehensive Monitoring
Use Azure Monitor, Application Insights, and Log Analytics to gain visibility into app performance and health.
- Set up alerts for CPU usage, memory, and error rates.
- Track user behavior and transaction flows.
- Use dashboards to visualize key metrics.
Proactive monitoring helps detect and resolve issues before users are affected.
Optimize for Performance and Cost
Regularly review app performance and resource utilization. Use Azure Advisor for personalized recommendations.
- Upgrade to newer VM sizes for better performance per dollar.
- Use auto-scaling to match demand.
- Archive cold data to Azure Blob Storage to reduce costs.
Continuous optimization ensures efficiency and reliability.
What are Azure apps?
Azure apps are applications built and hosted on Microsoft Azure’s cloud platform, including web apps, mobile backends, APIs, and serverless functions. They leverage Azure’s scalable infrastructure and integrated services for high availability and performance.
How much does it cost to run an Azure app?
Costs vary based on usage, but Azure offers a free tier and pay-as-you-go pricing. A basic web app can start at around $13/month, while complex applications with databases and AI services may cost more. Use the Azure Pricing Calculator for accurate estimates.
Can I deploy a custom domain with Azure apps?
Yes, Azure apps support custom domains and SSL certificates. You can map your domain (e.g., www.yourcompany.com) to your Azure app and enable HTTPS for secure connections.
Is Azure better than AWS for app development?
It depends on your needs. Azure excels in integration with Microsoft products and hybrid cloud scenarios, while AWS has a broader global footprint. For Windows-based or enterprise environments, Azure is often the preferred choice.
How do I secure my Azure app?
Use Azure AD for authentication, enable HTTPS, apply Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and integrate with Azure Security Center. Regularly update dependencies and follow the principle of least privilege.
Mastering Azure apps unlocks a world of possibilities for modern application development. From seamless scalability and robust security to AI integration and global reach, Azure provides the tools to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently. By following best practices and staying ahead of trends, organizations can leverage Azure apps to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge. Whether you’re just starting or scaling enterprise solutions, Azure apps offer a powerful, flexible, and future-ready platform.
Further Reading: